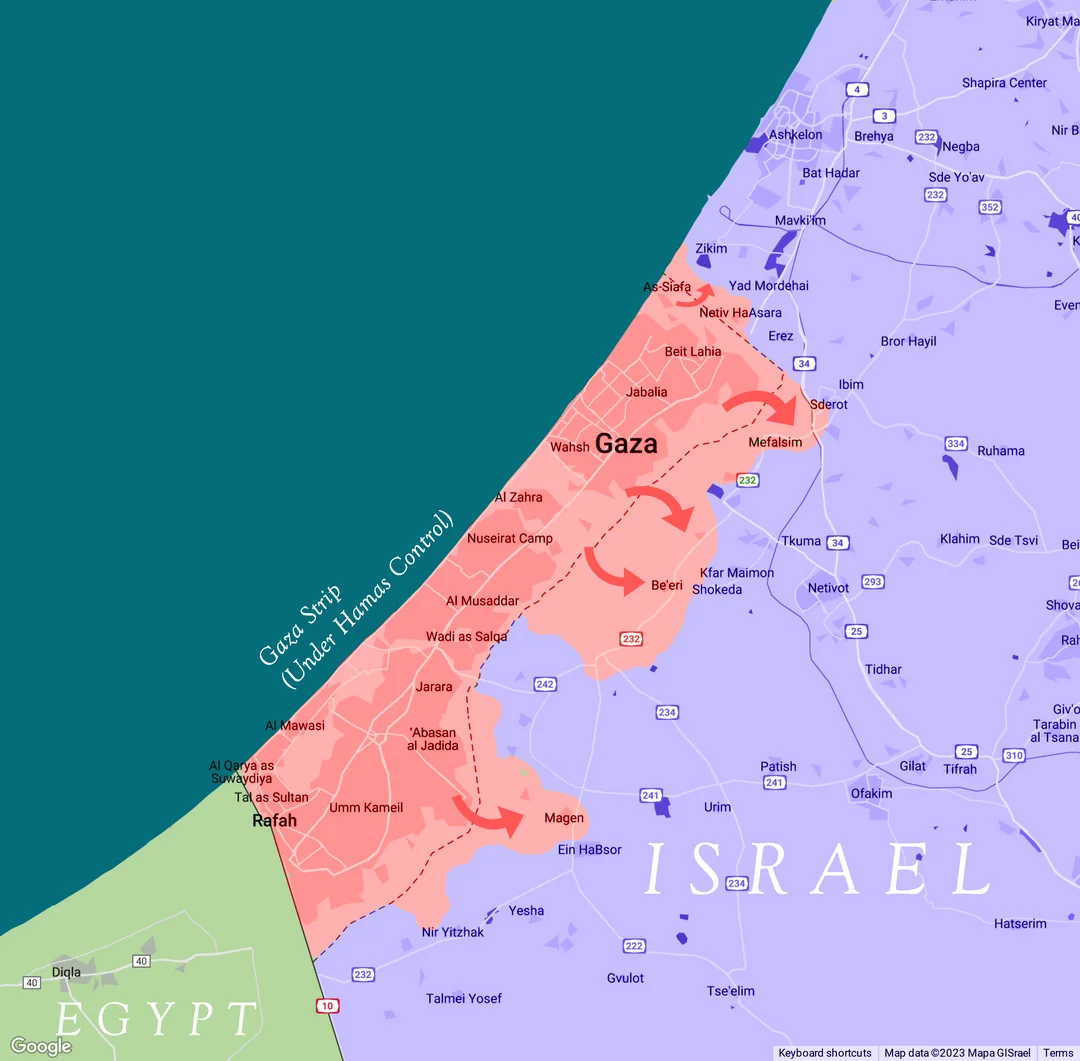
In the heart of the Middle East, amidst a complex web of historical events and geopolitical tensions, lies the region of Israel and the Gaza Strip. This article delves into the intricate history and ongoing conflicts that have defined the relationship between Israel and Hamas, the militant group governing Gaza. we aim to provide an in-depth understanding of the situation, the roots of the conflict, and the challenges faced by both sides.
The Setting: Kibbutz Eres, Southern Israel
Imagine standing in Kibbutz Eres, a small community in southern Israel, merely half a mile away from the Gaza Strip. This picturesque setting, marred by constant threats of Hamas terror attacks, paints a stark picture of life in this region. The 600 residents of this kibbutz live with the ever-present possibility of Hamas rockets raining down on their homes.
Table 1: Key Figures
| Location | Kibbutz Eres, Southern Israel |
|---|---|
| Population | 600 |
| Distance from Gaza Strip | Half a mile |
| Threat Level | Constant |
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) are a lifeline for these communities, working tirelessly to protect them and the 65,000 civilians living in the surrounding area. When the sirens wail, these people have a mere 15 seconds to find shelter, a testament to the relentless nature of the threat.
A Historical Perspective: How Did We Get Here?
Understanding the current situation requires delving into history. The roots of the Israel-Gaza conflict trace back to the aftermath of World War II. In 1947, the United Nations proposed a partition plan to divide the land into Jewish and Arab states. Israel accepted this plan, but the Arab nations rejected it, igniting a war. Gaza fell under Egyptian rule as a result.
Table 2: Timeline of Key Events
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1947 | UN Partition Plan proposed |
| 1948 | Arab rejection leads to war, Gaza under Egyptian rule |
| 1967 | Five Arab armies attack Israel, Gaza comes under Israeli control |
| 2005 | Israel unilaterally withdraws from Gaza |
| 2007 | Hamas takes control of Gaza, ousting Palestinian Authority |
In 1967, another significant turning point occurred when five Arab armies launched an attack on Israel. Israel successfully defended itself, and Gaza came under Israeli control. During this time, hundreds of terror attacks emanated from the Gaza Strip.
In 2005, Israel made a bold move by unilaterally and fully withdrawing from the Gaza Strip. IDF troops oversaw the removal of over 9,000 Israeli civilians from Gaza in a bid for peace. However, this withdrawal did not lead to the desired outcome; instead, it ushered in an era of rocket attacks and turmoil.
Hamas: The Unyielding Foe
To understand the current dynamics, it’s crucial to examine the role of Hamas, the governing authority in Gaza. Hamas, an internationally recognized terrorist organization, has consistently called for the destruction of Israel. Their charter explicitly states, “The day of judgment will not come about until Muslims fight Jews and kill them.”
Hamas’s actions speak louder than words. They have fired thousands of rockets into Israeli territory and executed numerous terrorist attacks, including suicide bombings, arson balloons, and drone attacks. Tragically, their tactics extend to terrorizing their own people, suppressing freedom of speech, and persecuting the LGBTQ+ community.
Table 3: Hamas’s Actions
| Action | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Firing Rockets | Threat to Israeli civilians |
| Suppression of Freedom | Limitation of civil rights within Gaza |
| Use of Human Shields | Endangerment of Palestinian civilians |
| Diverting Aid | Misallocation of resources meant for Gaza’s people |
Despite international calls for peace, Hamas remains steadfast in its hostility towards Israel. The Middle East Quartet, comprised of the UN, the European Union, the US, and Russia, set clear conditions for recognizing Hamas as the official government of Gaza, including renouncing violence and recognizing Israel’s right to exist. However, Hamas has consistently rejected these conditions.
The Humanitarian Challenge
Amidst the conflict, there is a humanitarian crisis in Gaza. Despite ongoing hostility from Hamas, Israel continues to provide humanitarian aid to the region. However, delivering aid is not without its challenges. In the recent escalation in May 2021, Hamas terrorists fired mortar shells at crossings used for bringing in humanitarian aid.
Table 4: Humanitarian Aid Challenges
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Hamas Attacks on Crossings | Disruption of aid delivery |
| Diversion of Resources | Aid meant for civilians diverted for terrorism |
Hamas’s actions not only disrupt aid delivery but also steal resources meant for the people of Gaza to further their terrorist agenda. This situation highlights the complexity of providing assistance in a conflict zone.
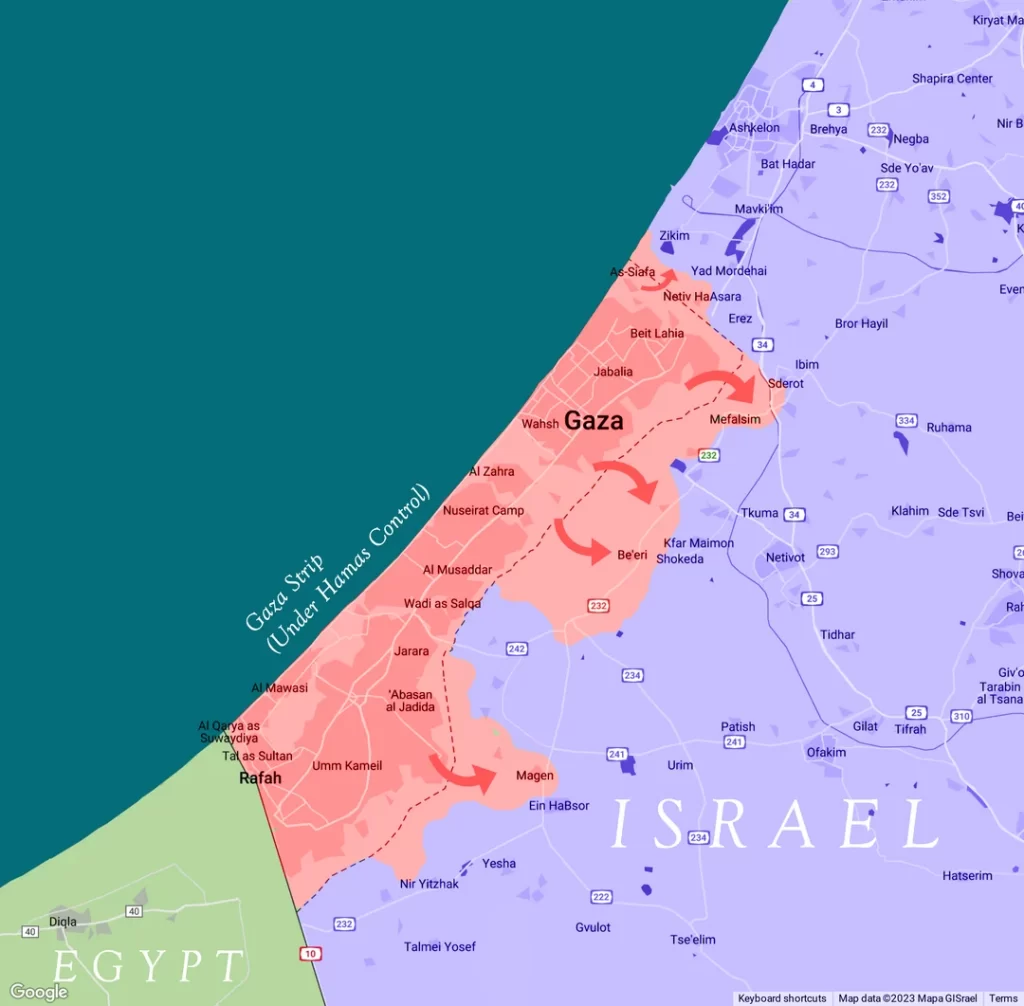
The Unending Threat: Current Scenario
Today, the threat persists. Hamas continues to launch rockets, arson balloons, and drones towards Israeli civilians. The security fences that crisscross the region are not just symbols but vital lifelines for protecting Israeli civilians.
Table 5: Current Scenario
| Threats | Israeli Response |
|---|---|
| Rocket Attacks | Vigilant defense and interception systems |
| Arson Balloons and Drones | Active monitoring and swift response |
| Security Fences | Essential protective barriers |
The IDF remains dedicated to safeguarding Israeli civilians from Hamas terrorism. However, it is essential to note that amidst this ongoing conflict, there is a glimmer of hope for a more peaceful future.
The Quest for Peace
While the IDF works tirelessly to protect civilians, Israel continues to hope for a future where all people in the region can coexist in peace and security. The path to peace, however, is fraught with obstacles.
Table 6: Factors Influencing Peace
| Factors | Impact |
|---|---|
| Hamas’s Intransigence | Hindrance to diplomatic negotiations |
| International Mediation | Role of global powers in peace negotiations |
| Humanitarian Efforts | Building trust through aid and cooperation |
One significant barrier to peace is Hamas’s refusal to engage in meaningful dialogue and its persistent calls for violence. International mediation plays a pivotal role in facilitating peace talks, with global powers exerting diplomatic pressure.
Despite the challenges, humanitarian efforts remain a beacon of hope. By providing aid and cooperating on essential issues, both sides can build trust and create an environment conducive to negotiations.
Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Landscape
The Israel-Gaza conflict is a multifaceted issue rooted in history, politics, and ideology. Kibbutz Eres, with its proximity to the Gaza Strip, serves as a microcosm of the larger conflict, where civilians live under constant threat. The IDF’s unwavering commitment to their protection is a testament to the resilience of those affected by this enduring struggle.
Table 7: Key Takeaways
| Key Takeaways | |
|---|---|
| Complex History | Rooted in post-WWII events and regional conflicts |
| Hamas’s Ideology | Driven by an uncompromising stance against Israel |
| Humanitarian Challenges | Aid delivery amid conflict poses significant hurdles |
| Hope for Peace | International mediation and humanitarian efforts offer glimmers of hope |
In this turbulent landscape, finding a path to lasting peace is a Herculean task. Yet, as history has shown, even the most entrenched conflicts can be resolved through dialogue, compromise, and the unwavering commitment to the well-being of all involved.
As we look to the future, we must remember that every step towards peace, no matter how small, brings us closer to a world where all people can live in harmony and security. The road may be long and arduous, but the desire for peace burns bright in the hearts of those who have endured the hardships of the Israel-Gaza conflict.